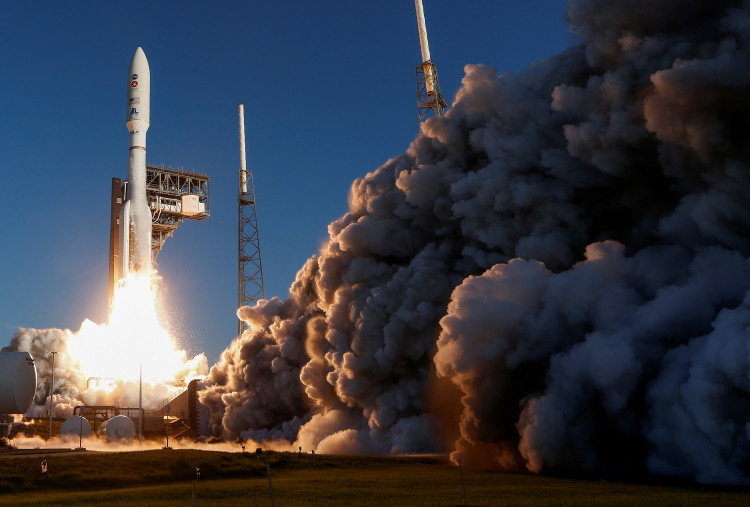
NASA has just awarded a $3.19 billion contract to build rocket boosters for future moon missions, which will be used on Artemis missions through 2031.
Space.com reports that the new deal builds on a prior 2020 contract that authorized Northrop Grumman to prepare for production and build twin boosters for the next six Space Launch System (SLS) megarocket flights after Artemis 3, taking the program all the way to Artemis 9.
According to NASA's contract statement, the award will assist the agency in planning and growing the Artemis program to meet future needs.
"The contract allows NASA to work with Northrop Grumman to not only build the boosters for upcoming missions, but also to evolve and improve the boosters for future flights," Bruce Tiller, SLS booster manager at NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center in Alabama, stated.
SLS is entrusted with delivering personnel throughout the solar system, beginning with flights to lunar orbit, the lunar surface, or the proposed lunar Gateway space station. It will make its maiden uncrewed flight in 2022. In 2024, the first crewed orbital trip will take place, followed by the first landing mission in 2025.
The rocket boosters that assist the NASA space shuttle during launches are the basis for the SLS booster technology. Between 1981 and 2011, solid rocket boosters were deployed on 135 space shuttle missions. Thiokol, subsequently known as ATK, was the original manufacturer. Thanks to a series of company mergers over the previous decade, Northrop Grumman now has the technology.
According to NASA documents, the SLS boosters are designed to be one-time use (not reusable, as the shuttle program requested) and incorporate a fifth segment in addition to the shuttle's four. According to Northrop Grumman's announcement regarding the new contract, more design upgrades to the shuttle program are already in the works, with the ninth mission of SLS expected to fly in 2019.
Northrop Grumman says that it has completed booster manufacture on Artemis 2 and that all segments for Artemis 3 boosters have been cast with propellant as of December 2021. Casting for the Artemis 4 segments began in November.
Other NASA contracts in support of moon missions are also being carried out by Northrop Grumman. The abort motor and attitude control motor for the Orion spacecraft's launch abort system, as well as a habitat and logistics outpost module for Gateway, are among the projects.
Northrop Grumman secured a nearly $50 million NASA letter contract in June 2020 to provide funding and authority for future booster orders. It allows for the production and operation of boosters for Artemis missions 4 through 8, as well as the evaluation of a new booster design for Artemis 9.