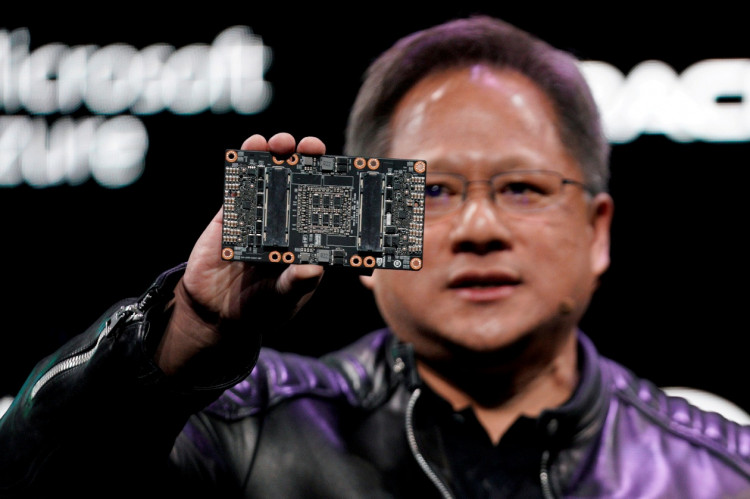
Nvidia Corporation, the American multinational technology company, is reportedly developing a version of its new flagship AI chips specifically designed for the Chinese market to comply with current U.S. export controls. This strategic move is seen as an effort to maintain its presence in China, which remains a significant market for the company despite ongoing geopolitical tensions and regulatory challenges.
The chip, tentatively named the "B20," is part of Nvidia's "Blackwell" chip series, which was unveiled in March and is scheduled for mass production later this year. The Blackwell series features cutting-edge processors, including the B200, which boasts performance capabilities up to 30 times faster than its predecessor in certain tasks such as generating responses from chatbots. This advancement underscores Nvidia's commitment to staying at the forefront of AI technology.
Nvidia plans to collaborate with Inspur, one of its major distributor partners in China, for the launch and distribution of the B20. According to sources familiar with the matter, shipments of the B20 are expected to commence in the second quarter of 2025. While Nvidia has not yet made an official announcement, the company's stock saw a 1.4% rise to $119.67 in premarket trading following the news.
The decision to develop a China-specific AI chip comes in response to the U.S. government's tightening of export controls on advanced semiconductors to China. These measures, implemented in 2023, aim to prevent China from achieving breakthroughs in supercomputing that could bolster its military capabilities. Since then, Nvidia has introduced three chips tailored for the Chinese market, demonstrating its ability to adapt to regulatory changes while continuing to innovate.
The introduction of the B20 is expected to help Nvidia fend off competition from Chinese technology giants like Huawei and startups such as Tencent-backed Enflame, which have been gaining traction in the domestic market for advanced AI processors. Despite these challenges, China accounted for approximately 17% of Nvidia's revenue in the fiscal year ending January, down from 26% two years earlier.
Nvidia's H20 chip, the company's most advanced AI chip for the Chinese market, initially faced a slow start when it was launched earlier this year. Priced below a competing chip from Huawei, the H20's sales have since picked up, with expectations that over 1 million units will be sold in China by the end of the year, generating an estimated $12 billion in revenue.
The ongoing geopolitical landscape and regulatory environment are likely to influence Nvidia's strategies moving forward. The U.S. is expected to continue applying pressure on semiconductor-related export controls, with efforts to persuade the Netherlands and Japan to impose further restrictions on chipmaking equipment to China. Additionally, the Biden administration is considering measures to regulate the most advanced AI models, such as those used in ChatGPT, to safeguard national security interests.
Global chip stocks experienced a decline last week following reports that the Biden administration was contemplating the implementation of the foreign direct product rule. This measure would enable the U.S. to prevent the sale of products manufactured using American technology, further complicating the landscape for international technology firms.