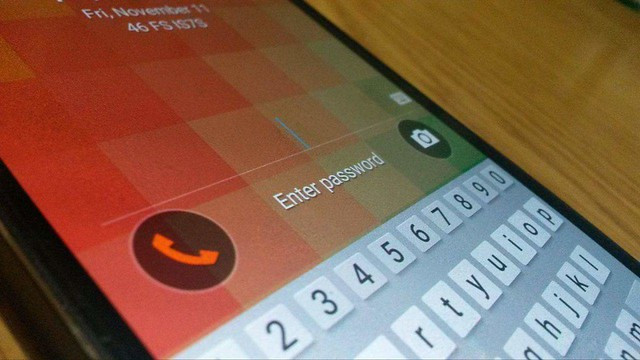
A few days ago, several tech sites reported about a bug in LastPass that enables websites to extract the previous password keyed in by the user the service's browser extension. According to reports, the bug was uncovered by Travis Ormandy, one of the researchers of Google's Project Zero. Fortunately, LastPass recently issued a statement claiming that it has already patched the malicious bug.
The LastPass bug was reported last August 29 through a bug report submitted by Travis Ormandy. On September 13, LastPass fixed the issue and released the update to all browsers where the fixes will be automatically applied. How does the bug work?
The malicious LastPass bug lures users into the malicious website and fools the browser extension to use a password from the website previously used by the visitor. According to Ormandy, the attackers could utilize a service like Google Translate to mask a malicious URL and fool users into visiting a rogue site. While LastPass said that the update should be automatically applied, users must check that they are using the most up-to-date service browser extension version.
This should be done particularly by those users with browsers that disable automatic updates for extensions. The malicious bug was patched by LastPass update version 4.33.0 of the extension. According to the company, the Opera and Chrome browsers were attacked by the bug but made it clear that it has already deployed the fix to all browsers as a kind of precaution.
LastPass could leak the last used credentials due to a cache not being updated. This was because you can bypass the tab credential cache being populated by including the login form in an unexpected way! https://t.co/bfLdDzSWS5 — Tavis Ormandy (@taviso) September 16, 2019
In a blog, LastPass modulated the severity of the most recent bug. According to Ferenc Kun, LastPass' security engineering manager, the exploit was dependent on the user visiting a malicious website and they are tricked into clicking on the page several times. The bug was relayed to LastPass before it was made public and so far, there is no evidence that an exploit was ever released on the web.
This boils down to the option of using a password manager for the sake of online security. The existence of this kind of bug underlines the sad truth that password managers, just like any other online service, can still be vulnerable to several security problems. It is always smart to use two-factor authentication to any sites that back it.
Also, it increases the level of the user's security if the password is unique is not used in other services. The company already made it clear that users do not need to do anything to their browser extension to resolve this bug since it was already deployed and applied to all browsers automatically.